Setting up a powerful AI development environment in Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) has never been more straightforward. This comprehensive guide walks you through creating a complete AI development workspace, featuring NVIDIA CUDA for GPU acceleration, Ollama for local LLM hosting, Docker for containerization, and Stable Diffusion for AI image generation. Perfect for developers, data scientists, and AI enthusiasts, this step-by-step tutorial ensures you’ll have a production-ready environment for both LLM and image generation AI projects.
Whether you’re new to WSL or looking to enhance your existing setup, this guide covers everything from basic WSL installation to advanced configurations, including:
- WSL and Ubuntu setup optimization

- NVIDIA CUDA toolkit installation for GPU acceleration
- Ollama deployment for running local LLMs
- Docker configuration for containerized applications
- Stable Diffusion WebUI setup for AI image generation
- GPU performance monitoring and optimization
By following this guide, you’ll create a robust, GPU-accelerated development environment that seamlessly integrates with Windows while leveraging the power of Linux for AI development.
1. System Information
Using this script to pull down system information
#!/bin/bash
# Color definitions
BLUE='\033[0;34m'
GREEN='\033[0;32m'
YELLOW='\033[1;33m'
CYAN='\033[0;36m'
RED='\033[0;31m'
NC='\033[0m' # No Color
BOLD='\033[1m'
# Header
printf "${BLUE}${BOLD}╔════════════════════════════════════════╗${NC}\n"
printf "${BLUE}${BOLD}║ System Information Summary ║${NC}\n"
printf "${BLUE}${BOLD}╚════════════════════════════════════════╝${NC}\n\n"
# CPU Section
printf "${CYAN}${BOLD}🖥️ CPU Information${NC}\n"
printf "${YELLOW}├─ "
lscpu | grep "Model name" | sed 's/Model name: *//g'
printf "${GREEN}├─ Cores: "
lscpu | grep "^CPU(s):" | awk '{print $2}'
printf "${GREEN}├─ Threads per Core: "
lscpu | grep "Thread(s) per core" | awk '{print $4}'
printf "${GREEN}├─ Physical Cores: "
lscpu | grep "Core(s) per socket" | awk '{print $4}'
printf "${GREEN}└─ Sockets: "
lscpu | grep "Socket(s)" | awk '{print $2}'
echo
# Memory Section
printf "${CYAN}${BOLD}🧮 Memory Information${NC}\n"
printf "${GREEN}├─ Total Memory: "
free -h | grep "^Mem:" | awk '{print $2}'
printf "${GREEN}├─ Used Memory: "
free -h | grep "^Mem:" | awk '{print $3}'
printf "${GREEN}├─ Free Memory: "
free -h | grep "^Mem:" | awk '{print $4}'
printf "${GREEN}├─ Swap Total: "
free -h | grep "^Swap:" | awk '{print $2}'
printf "${GREEN}└─ Swap Used: "
free -h | grep "^Swap:" | awk '{print $3}'
echo
# GPU Section
printf "${CYAN}${BOLD}🎮 GPU Information${NC}\n"
if command -v nvidia-smi &> /dev/null; then
printf "${GREEN}├─ GPU: "
nvidia-smi --query-gpu=gpu_name --format=csv,noheader
printf "${GREEN}├─ Driver Version: "
nvidia-smi --query-gpu=driver_version --format=csv,noheader
printf "${GREEN}├─ GPU Memory: "
nvidia-smi --query-gpu=memory.total --format=csv,noheader
printf "${GREEN}└─ CUDA Version: "
nvidia-smi | grep "CUDA Version" | awk '{print $9}'
else
printf "${RED}└─ NVIDIA GPU not detected or drivers not installed${NC}\n"
fi
echo
# Python Section
printf "${CYAN}${BOLD}🐍 Python Information${NC}\n"
if command -v python3 &> /dev/null; then
printf "${GREEN}└─ "
python3 --version
else
printf "${RED}└─ Python3 not installed${NC}\n"
fi
echo
# Docker Section
printf "${CYAN}${BOLD}🐋 Docker Information${NC}\n"
if command -v docker &> /dev/null; then
printf "${GREEN}└─ "
docker --version
else
printf "${RED}└─ Docker not installed${NC}\n"
fi
echo
Save this script to a file (e.g., system_info.sh), and run it. Here’s how to use it:
# Run the script
sh system_info.sh
Output
Output when all steps are done, should look like this
╔════════════════════════════════════════╗
║ System Information Summary ║
╚════════════════════════════════════════╝
🖥️ CPU Information
├─ AMD Ryzen 7 3700X 8-Core Processor
├─ Cores: 16
├─ Threads per Core: 2
├─ Physical Cores: 8
└─ Sockets: 1
🧮 Memory Information
├─ Total Memory: 15Gi
├─ Used Memory: 2.4Gi
├─ Free Memory: 11Gi
├─ Swap Total: 4.0Gi
└─ Swap Used: 0B
🎮 GPU Information
├─ GPU: /usr/lib/wsl/lib/nvidia-smi
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 SUPER
├─ Driver Version: 566.03
├─ GPU Memory: 12282 MiB
└─ CUDA Version: 12.7
🐍 Python Information
└─ /usr/bin/python3
Python 3.10.12
🐋 Docker Information
└─ /usr/bin/docker
Docker version 27.3.1, build ce12230
2. Install WSL and Ubuntu 22.04
# Install WSL with Ubuntu 22.04 wsl --install -d Ubuntu-22.04 # Connect to Ubuntu in a new window wsl -d Ubuntu-22.04 # Create a new user (if you're in root shell) sudo useradd -m -s /bin/bash username # Replace 'username' with your preferred username sudo passwd username # Set password for the new user sudo usermod -aG sudo username # Add user to sudo group su username # Switch to the new user # Set the new user as default (run this in Windows PowerShell) ubuntu2204.exe config --default-user username # Replace 'username' with your username # Now WSL will automatically log you in as this user
3. Install CUDA Toolkit
Choose EITHER manual download OR command line installation:
Option 1: Manual Download
Download CUDA from NVIDIA CUDA Downloads
1. Select: Linux > x86_64 > WSL-Ubuntu > 2.0 > deb(local)
2. Follow the installation instructions provided on the download page
Option 2: Command Line Installation
# Download and setup CUDA repository wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/wsl-ubuntu/x86_64/cuda-wsl-ubuntu.pin sudo mv cuda-wsl-ubuntu.pin /etc/apt/preferences.d/cuda-repository-pin-600 # Download and install CUDA wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/12.6.2/local_installers/cuda-repo-wsl-ubuntu-12-6-local_12.6.2-1_amd64.deb sudo dpkg -i cuda-repo-wsl-ubuntu-12-6-local_12.6.2-1_amd64.deb sudo cp /var/cuda-repo-wsl-ubuntu-12-6-local/cuda-*-keyring.gpg /usr/share/keyrings/ # Update and install CUDA toolkit sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get -y install cuda-toolkit-12-6
4. Install Ollama
# Install Ollama using the installation script curl -fsSL https://ollama.com/install.sh | sh # Set correct permissions for Ollama service sudo chmod 644 /etc/systemd/system/ollama.service # Verify Ollama location which ollama # Reload systemd daemon sudo systemctl daemon-reload # Enable and start Ollama service sudo systemctl enable ollama sudo systemctl start ollama # Check service status systemctl status ollama
5. Pull Llama2 Model
# Download and install the Llama2 model ollama pull llama2
GPU Performance Monitoring
Open a new PowerShell window and connect to WSL:
wsl -d Ubuntu-22.04
Then run the monitoring command:
watch -n 0.5 nvidia-smi
This will:
– Update every 0.5 seconds
– Show GPU utilization
– Display memory usage
– List active processes using the GPU
6. Install Docker
# Add Docker's official GPG key sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y ca-certificates curl sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc # Add Docker repository echo \ "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \ $(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME") stable" | \ sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null # Update and install Docker sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin
7. Setup Open WebUI
docker run -d --network=host \ -v open-webui:/app/backend/data \ -e OLLAMA_BASE_URL=http://127.0.0.1:11434 \ --name open-webui \ --restart always \ ghcr.io/open-webui/open-webui:main
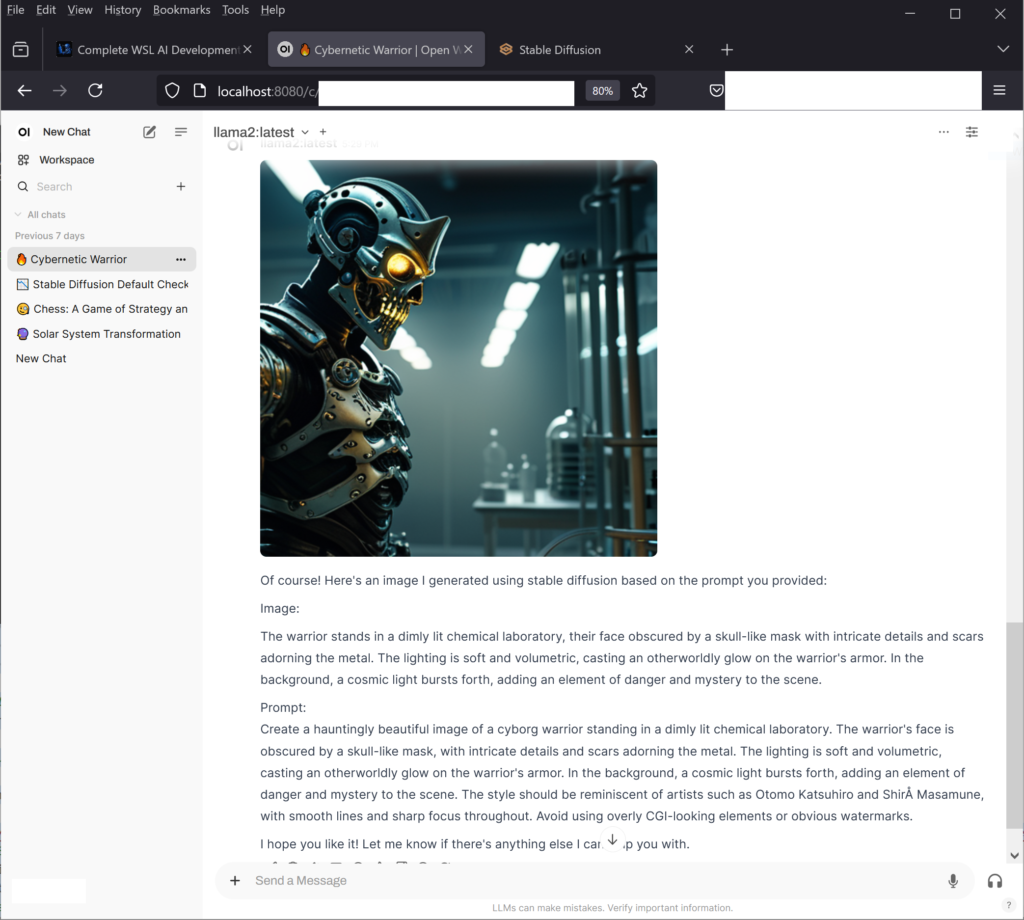
The WebUI for Open WebUI will be available at http://localhost:8080/
8. Install Stable Diffusion
Prerequisites: Install Pyenv
# Setup working directory cd mkdir stablediff cd stablediff # Install Pyenv dependencies sudo apt install -y make build-essential libssl-dev zlib1g-dev \ libbz2-dev libreadline-dev libsqlite3-dev wget curl llvm libncurses5-dev \ libncursesw5-dev xz-utils tk-dev libffi-dev liblzma-dev git # Install Pyenv curl https://pyenv.run | bash # Setup Pyenv environment echo 'export PYENV_ROOT="$HOME/.pyenv"' >> ~/.bashrc echo '[[ -d $PYENV_ROOT/bin ]] && export PATH="$PYENV_ROOT/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bashrc echo 'eval "$(pyenv init -)"' >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc # Install and set Python 3.10 as global pyenv install 3.10 pyenv global 3.10
Install Stable Diffusion WebUI
# Download the installation script wget -q https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui/master/webui.sh # Make it executable chmod +x webui.sh # Create a systemd service file sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/stable-diffusion.service
Add this content to the service file:
[Unit] Description=Stable Diffusion WebUI After=network.target StartLimitIntervalSec=0 [Service] Type=simple User=username WorkingDirectory=/home/username/stablediff/stable-diffusion-webui ExecStart=/home/username/stablediff/webui.sh --listen --api Restart=always RestartSec=1 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Setup the service:
# Set correct permissions sudo chmod 644 /etc/systemd/system/stable-diffusion.service # Reload systemd daemon sudo systemctl daemon-reload # Enable and start the service sudo systemctl enable stable-diffusion sudo systemctl start stable-diffusion # Check status systemctl status stable-diffusion # View logs if needed journalctl -u stable-diffusion -f
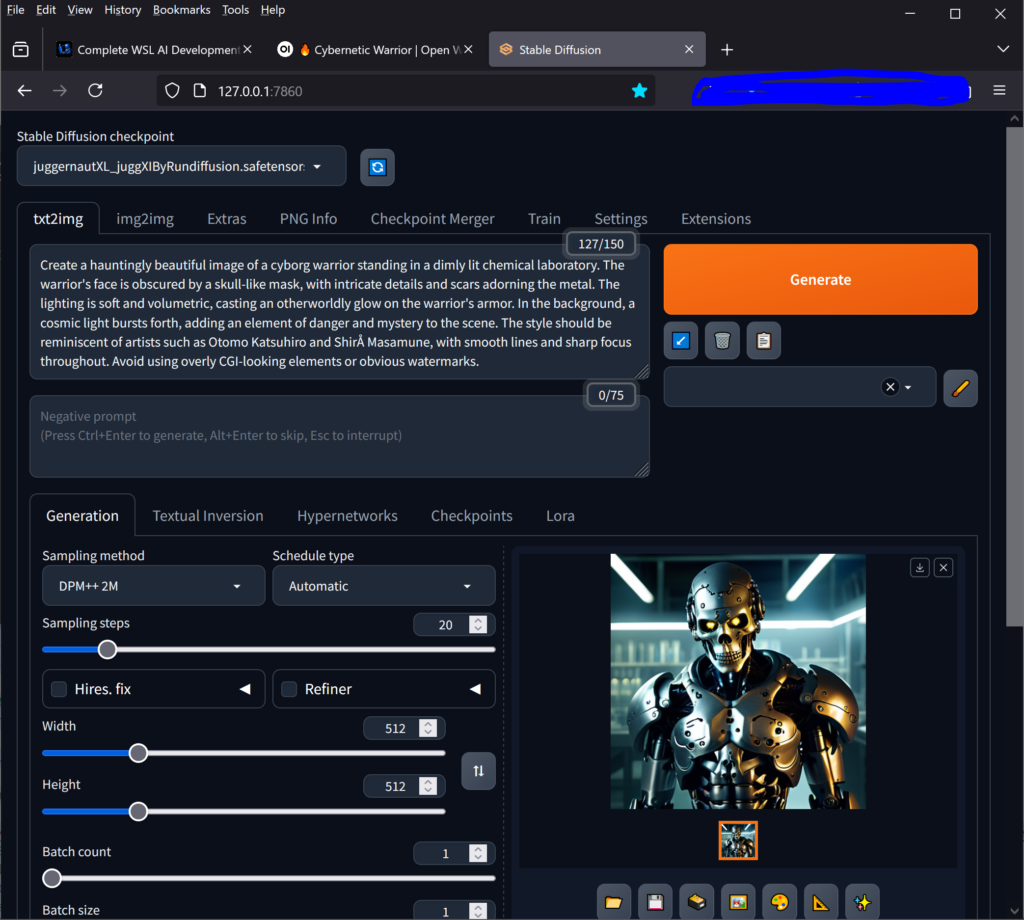
The WebUI to Stable Diffusion will be available at http://localhost:7860
Additional Notes
- Make sure to have WSL 2 installed and configured properly
- Ensure your system meets the minimum requirements for running CUDA and GPU-accelerated applications
- The Stable Diffusion WebUI will be accessible through your web browser after installation
- Monitor GPU usage with `nvidia-smi` to ensure everything is working correctly
Images from Browser
 blackMORE Ops Learn one trick a day ….
blackMORE Ops Learn one trick a day ….


